|
Topic Covers: G20 17th
India’s
About
|
Relevance: For UPSC CSE Prelims as well as Mains Exams (General
Studies II: International Relation).
G20 Summit:
“Vasudhaiv Kutumbakam’ is signature of India’s
compassion to world. Lotus portrays cultural heritage and faith of India in
bringing world together”
PM Narendra Modi
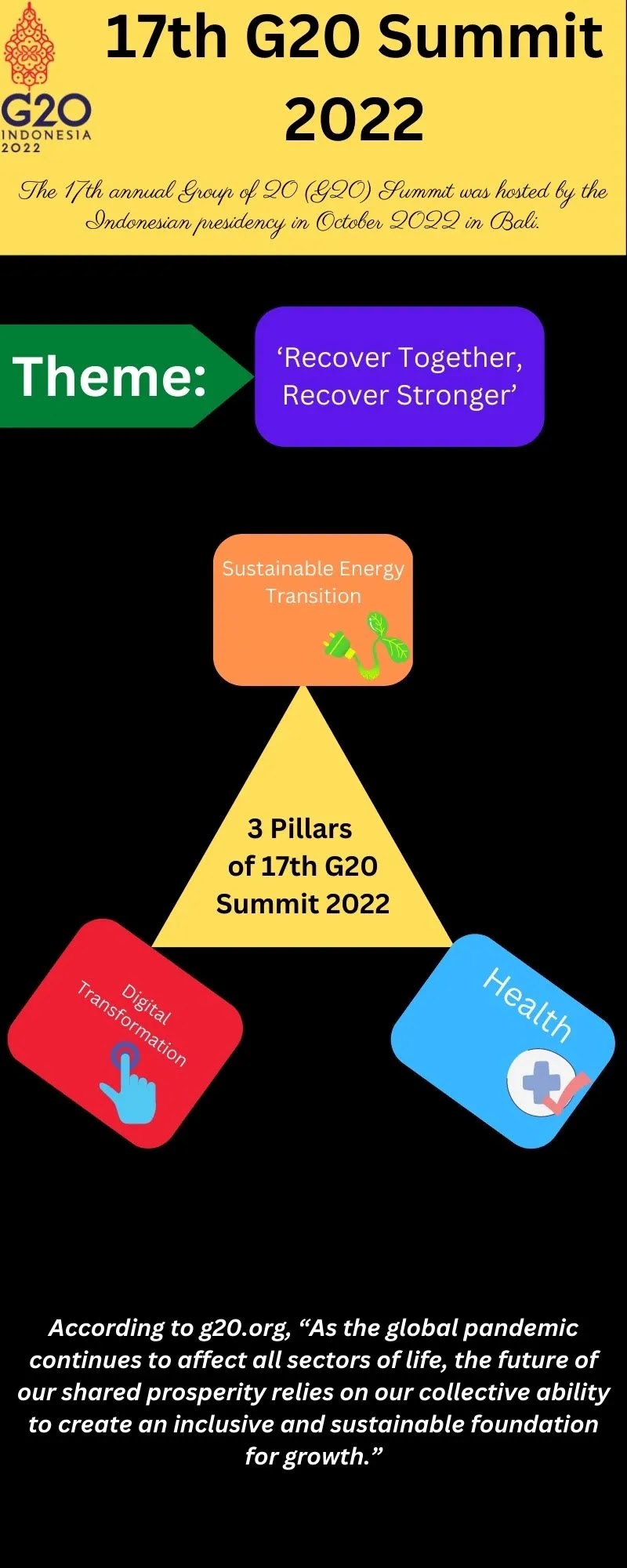
17th G20 Summit 2022:
The 17th annual Group of 20 (G20) Summit was
hosted by the Indonesian presidency in October 2022 in Bali.
Theme: ‘Recover Together, Recover Stronger’
According to g20.org, “As the global pandemic continues to
affect all sectors of life, the future of our shared prosperity relies on our
collective ability to create an inclusive and sustainable foundation for
growth.”
Three Pillars of 17th G20 Summit 2022:
- Global Health Architecture: To making the global health
system more inclusive, equitable, and responsive to crises. - Sustainable Energy Transition: To accelerate the transition
towards cleaner energy sources through the various platforms for investment. - Digital Transformation: Through establishing a new framework
for international cooperation, on realising the full potential of the world
economy’s accelerating digitalization.
Now, India has assumed the Presidency of the G20 from 1
December 2022 to 30 November 2023.
18th G20 Summit 2023 in Context of India:
India holds the Presidency of the 18th annual G20
Summit from December 1, 2022 to November 30, 2023.
- India’s G20 Presidency will work to promote this universal
sense of one-ness.
Theme: “One Earth, One Family, One Future” (or) “Vasudhaiva
Kutumbakam”
- The theme also highlighted LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment).
Logo:
- The G20 Logo reflects the vibrant colours of India’s
national flag – saffron, white and green, and blue. - It shows planet Earth with the lotus, India’s national
flower that symbolised growth amid challenges. - The Earth reflects India’s pro-planet approach to life, one
in perfect harmony with nature. - Below the G20 logo is “Bharat”, written in the Devanagari
script.
Agenda: India’s agenda at the G-20 as “inclusive, ambitious,
action-oriented”.
Guest Nations: India’s special invitee guest countries are
Bangladesh, Egypt, Mauritius, Netherlands, Nigeria, Oman, Singapore, Spain and
UAE.
Key Priorities of India’s G20 Presidency:
Environment:
- Climate Change: Focus on climate finance and technology and
ensuring just energy transitions for developing nations across the world. - India offers the world LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) – to
adopt environmentally-conscious practices.
Accelerated, Inclusive & Resilient Growth:
These are a cornerstone for sustainable development. India
aims to accelerate integration of MSMEs in global trade, bring in the spirit of
trade for growth, promote labour rights and secure labour welfare, address
global skills gap, and build inclusive agricultural value chains and food
systems etc.
Achieve SDGs:
Due to impact of COVID-19, India wants to focus on
recommitting G20’s efforts to achieving the targets laid out in the 2030 Agenda
for Sustainable Development.
Digital Transition:
India can approach towards a human-centric technology, and
facilitate greater knowledge-exchange in priority areas like digital public
infrastructure, financial inclusion, and tech-enabled development in sectors
ranging from agriculture to education.
Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century:
Multilateralism can create more accountable, inclusive just,
equitable and representative multipolar international system that is fit for
addressing the challenges in the 21st century.
Women:
- Women empowerment and representation being at the core of
India’s G20 deliberations. - This includes a focus on bringing women to the fore, and in
leading positions, in order to boost socio-economic development and achievement
of SDGs.
G20 Trioka:
The Presidency is supported by the Troika – previous,
current and incoming Presidency. From December 1, 2022 India’s Presidency, the
troika will comprise Indonesia, India and Brazil, respectively.
About G20 Summit:
The Group of Twenty (G20) is the most important platform for
global economic cooperation. Regarding all significant worldwide economic
concerns, it is important in building and enhancing global governance.
Aim: To secure global financial stability.
Founded:
- The G20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis
as a forum for the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to discuss
global economic and financial issues. - In the wake of the world financial and economic crisis in
2007, it was upgraded to the level of heads of state or government, and in 2009
it was given the title of “premier forum for international economic
cooperation.”
G20 Members:
The Group of Twenty (G20) comprises 19 countries (Argentina,
Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy,
Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Türkiye,
United Kingdom and United States) and the European Union.
- The G20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over
75% of the global trade, and about two-thirds of the world population.
Invited International Organisations:
The regular International Organisations (UN, IMF, WB, WHO,
WTO, ILO, FSB and OECD) and Chairs of Regional Organisations (AU, AUDA-NEPAD
and ASEAN), India, as G20 Presidency, will be inviting ISA, CDRI and ADB as
Guest IOs.
G20 Summit:
The G20 Summit is held annually, under the leadership of a
rotating Presidency.
The G20 initially focused largely on broad macroeconomic
issues, but it has since expanded its agenda to inter-alia include trade,
climate change, sustainable development, health, agriculture, energy,
environment, climate change, and anti-corruption.
UPSC Civil Services Examination,
|
References:
PIB, The Indian Express, g20.org


.png)