UPSC Geography Questions on Tropical and Temperate Cyclones:
Que 2. Make a comparative study of the temperate and tropical cyclones.
Que 3. Que. Compare and contrast tropical cyclones and temperate cyclones.
Que 4. Discuss critically the characteristics of the tropical cyclones and analyse the extent to which differ from the temperate cyclones.
Que 5. Discuss the tropical cyclones and analyze the differences between tropical and temperate cyclones.
Cyclones ~
Condition for Tropical and Temperate Cyclones Formation ~
Two types of Cyclone ~
1. Tropical Cyclones ~
Characteristics of Tropical Cyclone ~
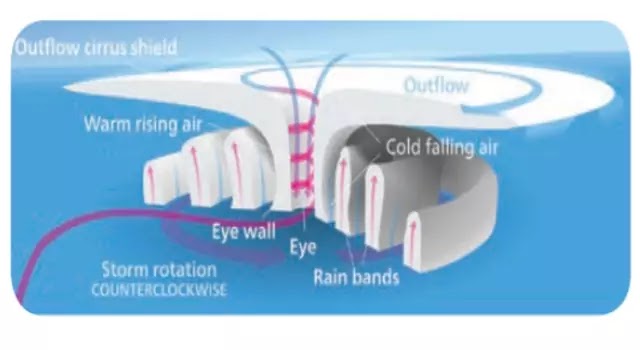
* The Central area of tropical cyclone is known as 'Eye' of the Cyclone.*The diameter of tropical cyclone varies from 150 to 500 km and vertically from surface to about 12 km.
* The isobar of tropical cyclones are circular in shape and pressure gradient is very steep.
* They occur in Northern hemisphere in the autumn season.
The favourable condition for formation of Tropical Cyclones ~
Stages of Development of Tropical Cyclone:
As per the criteria adopted by the World Meteorological
Organisation (W.M.O.), India Meteorological Department classifies the low
pressure systems in to vary classes based on wind speed.
1. Tropical Disturbances
2. Tropical depressions Low winds with a speed between 31
and 61 km ph.
3. Tropical cyclone wind speed from 62 to 88 km ph and it is
assigned a name.
4. Severe Cyclonic Storm (SCS) wind speed is between 89 to
118 km ph
5. Very SCS wind speed between 119 to 221 km ph and
6. Super Cyclonic Storm when wind exceeds 221 km ph.
Origin of Tropical Cyclone:
Tropical cyclones have certain mechanism for their
formation. These are
A source of warm, moist air derived from tropical oceans with sea surface temperature normally near to or in excess of 27 °C.
Structure of Tropical Cyclone:
Wind near the ocean surface is blowing from different
directions converging and causing air to rise and storm clouds to form.
Winds which do not vary greatly with height are known as low
wind shear. This allows the storm clouds to rise vertically to high level;
Landfall:
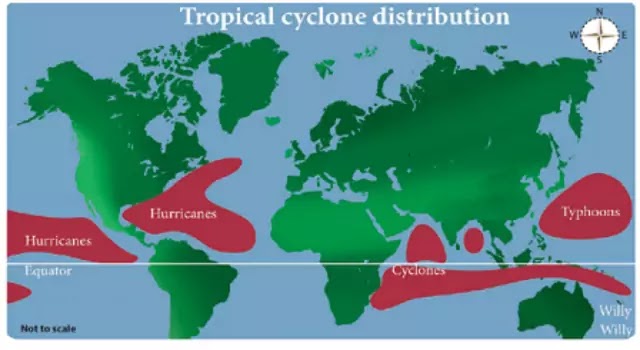
Regional Name of Cyclones ~
Despite the huge loss of property, animals and human life during the cyclone, there are some advantage of tropical cyclones ~
• The streams are flushed of pollution.
• They add moisture to dry soil conditions.
• The local water bodies are restored.
• These Precipitation help to maintaining the water budget
• The rainfall recharges ponds, lakes underground water table.
 |
| Mind Map of Tropical Cyclone |
Temperate / Extra Tropical Cyclones ~
The cyclone formed in the mid latitudes is called as temperate cyclone. As they are formed due to movement of air masses and front, they are called as ‘Dynamic cyclone’ and ‘Wave cyclone’. This cyclone is characterised by the four different sectors, which are varied with their weather patterns.
Formation of Temperate Cyclone:
Stages in the Formation of Temperate Cyclone:
a. Frontogenesis –Formation of front due to collision of two contrasting air masses.
b. Cyclone genesis – Formation of cyclone due to conversion of fronts into various sectors.
c. Advancing Stage – The stage where cold front advances towards warm front.
d. Occlusion stage - The stage where the cold front over takes warm front
e. Frontalysis – The last stage where fronts disappear and cyclone ends its life.
Most Cyclone Prone Countries ~
Differences between Tropical and Temperate Cyclones :
The Isobar of tropical cyclone are circular and pressure gradient is very steep.
Temperate cyclone isobars are V-shaped and pressure gradient is gentle.
* Moving Direction -
Temperate Cyclone move from west to east under the influence of westerly.
* Wind Velocity -
The Wind velocity of tropical cyclone is higher (200 kilometre per hour to 300 km per hour, which may increases up to 1200 km per hour).
While temperate cyclone wind velocity is lower (40 to 60 km per hour).
* Rainfall -
Tropical cyclone give torrential rainfall in shorter time.
Temperate cyclone give lower rainfall continue for many days.
* Source of Energy -
Tropical cyclone source of energy is latent heat of condensation.
Temperate cyclone source of energy is different in density of air masses.
* Front Formation -
In tropical cyclone front formation not indispensable.
In temperate cyclones friends formation is dispensable.
* Atmospheric Relation -
the relationship of tropical cyclone with upper atmosphere is not very clear.
The relationship of temperate cyclone is very clear with upper atmosphere that is jet stream.
* Latitudes -
Tropical cyclone which are found between 5 degree North and South to 25 degree North and South.
Temperate cyclone found between 35 degree North and South to 65 degree North and South.
3 Prime category for Cyclone Management ~
1. Pre- Phase -* Prevention
* Mitigation
* Preparedness
These steps taken before the the natural hazard of Cyclones. It include long-term prevention measures like construction of embankment to prevent flooding increasing plantation for reducing occurrence of landslide & sound environment management.
cyclone can also be mitigate through various short-term measures which either reduce our modify the scale and intensity of the thread improve the durability and capacity of elements at risk, e.g. proper maintenance of drainage system, better awareness and public education to reduce the risk of hazards, etc.
2. During Cyclones -
* Evacuation
* Search
* Rescue
During the cyclone, require speedy response to elevate and minimise suffering and losses. The evacuation, Search and rescue followed by provision of basic needs such as food clothing, shelter, medicine, and other necessity essential to bring the life of effective community back to degree of normalcy.
3. Post Cyclonic Phase -
* Recovery : to achieve early recovery and reduce vulnerability and future risk.
* Rehabilitation : includes provision of temporary public utilities and housing as interim measure to assist long-term recovery.
* Reconstruction : include construction of damaged infrastructure and habitats and enabling sustainable livelihoods.



1 Comments
All doubts cleared regarding Cyclones. Thanks you Sir !
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Thanks...keep in touch 🤟