A solar
photovoltaic (SPV) technology is used to converts fraction of solar radiation
into electrical energy.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Technology consist of:
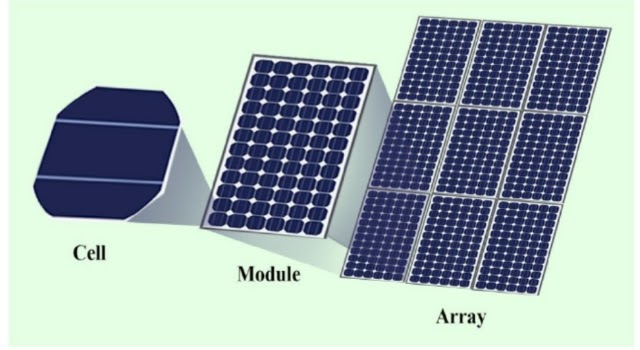
A SPV module is made of specific number of solar cells generally connected in series. The series and parallel combination of modules serve two purposes. The number of modules connected in series generates the required voltage suitable to supply power to the controller and the number of modules in parallel generates the required current to drive the motor and pump.
A Solar PV array consists of number of modules which are connected into series and parallel configuration to provide required voltage and current to drive a specific load(s).
SPV module has two polarities positive (+) and negative (-) and when exposed to Sun, generates Direct Current (DC) electricity. The current flows from positive (+) to negative (-) terminals of the SPV Module, or SPV array. This electricity so produced which is in the form of DC power, can either be used in this form directly or converted into Alternating Current (AC). As we know, Alternating Current (AC) is generally used for domestic purposes.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Technology consist of:
A. Solar cells:
Solar cells is a p-n junction semiconductor device made of silicone which is generally used to fabricate semiconductor chips of the computer and other electronic devices. When sunlight hits the cells, the solar cell generates Direct Current (DC) electric power. A silicon solar cell normally generates 0.6V DC and about 8A Current depending on the area. Therefore, a solar cell of 6 inches can generates power up to 5 watts at the present-day technology.B. Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) Module:
Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) Module converts fraction of solar radiation into electrical energy. SPV module is a single mono block unit having a fixed number of solar cell strings (36, 72 etc.), which is the fundamental building block of SPV systems. It consists of Solar cell strings sealed between the layers of Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA).A SPV module is made of specific number of solar cells generally connected in series. The series and parallel combination of modules serve two purposes. The number of modules connected in series generates the required voltage suitable to supply power to the controller and the number of modules in parallel generates the required current to drive the motor and pump.
A Solar PV array consists of number of modules which are connected into series and parallel configuration to provide required voltage and current to drive a specific load(s).
SPV module has two polarities positive (+) and negative (-) and when exposed to Sun, generates Direct Current (DC) electricity. The current flows from positive (+) to negative (-) terminals of the SPV Module, or SPV array. This electricity so produced which is in the form of DC power, can either be used in this form directly or converted into Alternating Current (AC). As we know, Alternating Current (AC) is generally used for domestic purposes.
Also Read: International Solar Alliance
C. Solar PV Array:
A photovoltaic (PV) array is the complete power generating unit consisting of SPV module. Solar PV array consists of parallel and series combination of identical photovoltaic (PV) 9 modules to generate the required power (kWp) to operate any electrical appliance/ equipment. Since this programme is on solar PV water pumping system, electric appliance in this case implies to the solar water pump and its connected motor.D. Types of PV Modules:
Three major technology types of modules used in solar PV applications. The technology is classified based on its manufacturing technology such as wafer based or thin films, and the type of semiconductor material such as Si (silicon), A-Si (arsenic silicon), Cd-Te (cadmium-telluride) and CIGS (copper, indium, gallium, selenide).1. If the solar arrays consist of identical modules connected in parallel, the 10 output current will increase and voltage remain same as that of the single module.
2. If the solar arrays consist of identical modules connected in series, the output voltage will increase whereas current remain same as that of the single module.
(a) Series Connection of Solar Modules:
Three solar modules (37 volts/8 amps each) are connected in series. In this connection voltages add up as given below:37+37+37=111 volts (approximately)
It must be noted for either series connection or in a parallel connection the type, capacity, make etc. of solar modules should be IDENTICAL to enable the system to function properly.
(b) Parallel Connection of Solar Modules:
In parallel connection of solar modules, the voltage output would remain then same but the current would add up and increase as shown in the figure 2.8.This connection is employed where the high currents are required.
Three solar modules (37V/ 8A each) are connected in parallel. The negative of the first solar module is connected to the negative of the next solar module, and the following panels follow suit. The terminals at the end comprise of the positive terminals of all modules and the negative 11 terminals of all the modules. In this connection current add up and voltage remains the same.
8+8+8=24 Amps
Advantages of Solar PV Technology:
Major Advantages of SPV Technology are as follows:- Clean energy source
- Since it uses sunlight as input, no fuel cost incurred.
- As long as solar radiation is available the power to drive the motor & pump will available.
- Since it is standalone system its operation is not affected or disturb by other loads operating nearby unlike grid-based pumping system.
- The modularity makes it easy for being constructed in sizes as required.
- Ease of installation and transportation.
- Minimal maintenance required and has long life span (more than 25 years).
- Long operation life and no wear and tear as there are no moving parts.
Limitations:
The major limitation of solar PV technology is the capex (capital expense) cost is apparently high. The power available could be intermittent and affected by moment of the cloud. Without storage, it is not possible to use the solar pumpsin night time.
Applications Solar PV
Technology:
Power
Supply: Power
supply for household use, industrial and agricultural use, etc.
Residential: Indoor and outdoor lighting system, electrical equipment, electric gate opener, security system, ventilator, water pump, water filter, emergency light, etc.
Lighting System: Traffic signalling system, telephone booth lighting, billboard lighting, parking lot lighting, street lighting, lighting in remote areas etc.
Water supply: Irrigation, drinking water, livestock watering, agriculture, gardening and farming, mining, public utility etc.
Battery charging system: Emergency power system, battery charging centres etc.
Agriculture: Water pumping, agricultural products fumigator, thrashing machines, water sprayer, insect trap lighting etc.
Fishing: Water pumping, oxygen filling system for fish-farming etc.
Health center: Refrigerator and cool box for keeping medicines and vaccines, medical equipment, etc.
Communication: Air navigational aid, air warning light, lighthouse, beacon navigation aid, illuminated road signage, railway crossing signals, emergency telephone etc.
Telecommunication: Microwave repeater station, telecommunication equipment,
portable communication equipment (e.g. communication radio for service and military exercise), weather monitoring station, etc.
Remote area: Power supply in remote areas like hill, island, forest and remote area where the utility grids are not available, solar water purification, wild life fencing.
Space: Satellite, international space station, spacecraft, etc.
Energy Parks: The large mega scale power plants feeding power to ultrahigh voltage grids.
Rooftop: Solar PV systems installed on the roof of house, industries, govt buildings, large industrials roofs etc. feed power to HT and LT grids.
Applications Solar PV
Technology:
Power
Supply: Power
supply for household use, industrial and agricultural use, etc.Residential: Indoor and outdoor lighting system, electrical equipment, electric gate opener, security system, ventilator, water pump, water filter, emergency light, etc.
Lighting System: Traffic signalling system, telephone booth lighting, billboard lighting, parking lot lighting, street lighting, lighting in remote areas etc.
Water supply: Irrigation, drinking water, livestock watering, agriculture, gardening and farming, mining, public utility etc.
Battery charging system: Emergency power system, battery charging centres etc.
Agriculture: Water pumping, agricultural products fumigator, thrashing machines, water sprayer, insect trap lighting etc.
Fishing: Water pumping, oxygen filling system for fish-farming etc.
Health center: Refrigerator and cool box for keeping medicines and vaccines, medical equipment, etc.
Communication: Air navigational aid, air warning light, lighthouse, beacon navigation aid, illuminated road signage, railway crossing signals, emergency telephone etc.
Telecommunication: Microwave repeater station, telecommunication equipment,
portable communication equipment (e.g. communication radio for service and military exercise), weather monitoring station, etc.
Remote area: Power supply in remote areas like hill, island, forest and remote area where the utility grids are not available, solar water purification, wild life fencing.
Space: Satellite, international space station, spacecraft, etc.
Energy Parks: The large mega scale power plants feeding power to ultrahigh voltage grids.
Rooftop: Solar PV systems installed on the roof of house, industries, govt buildings, large industrials roofs etc. feed power to HT and LT grids.
Also Read: Solar Energy
Source : Swayam


1 Comments
Really explains everything in detail, the article is very interesting and effective. Thank you and good luck with the upcoming articles.What is Manufacturing Technology?
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Thanks...keep in touch 🤟