- What is Energy Crisis?
- Why in News?
- What are the factors of recent energy crisis occurs?
- History of energy crisis/Phases of energy crisis.
- What are the Various Dimensions of Energy Crisis?
- What are the Causes of Energy Crisis?
- What are the Impact of Energy Crisis?
- What are the Solutions for Energy Crisis?/How to overcome from energy crisis?
- Conclusion
|
UPSC Based
Mains Questions on World Energy Crisis:
|
Why in News?
According to the IEA latest Report 2022, the global energy
crisis triggered by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is causing profound and
long-lasting changes that have the potential to hasten the transition to a more
sustainable and secure energy system.
- For the first time, global demand for each of the fossil fuels shows a peak or plateau across all WEO (World Energy Outlook) scenarios, with Russian exports in particular falling significantly as the world energy order is reshaped.
Recent Energy Crisis occur due to a variety of Factors:
- Russia began withholding gas supplies to Europe in 2021, months ahead of its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
- Russia has increasingly curtailed or even turned off its export pipelines. Russia is by far the world’s largest exporter of fossil fuels, and a particularly important supplier to Europe.
- The rapid economic recovery, weather conditions in various parts of the world, maintenance work that had been delayed by the pandemic.
- The decisions of oil and gas companies and exporting countries to reduce investments.
- Because to increased EV (Electric Vehicles) sales, oil demand will peak in the mid-2030s and then begin to decline modestly through the middle of the century.
- Due to increase focus on renewable energy based technologies such as solar PV, wind, EVs and batteries also reduce the demand of fossil fuels.
- In the WEO's more climate-focused scenarios, the reductions occur considerably more quickly and sharply.
What is Energy Crisis?
- Energy crisis has a geo-political origin. Energy crisis doesn't necessarily mean the lack of resources, it indicates disequilibrium in the supply and demand mechanism.
- Energy crisis in geography must include all the energy resources not petroleum alone but petroleum constitutes more than two third of energy requirements of the world.
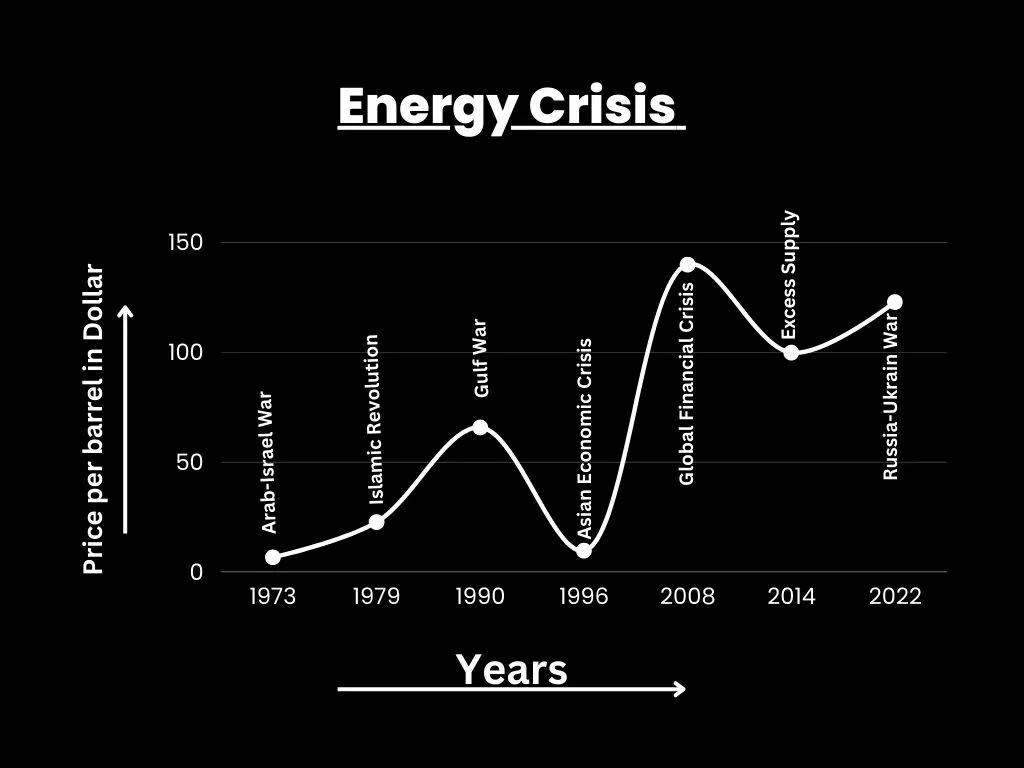
History of Energy Crisis:
Energy is the fundamental resource which runs the economic
wheels of the world. In 1973 the petroleum price was raised from 1.5 dollar per
barrel to 7 dollar per barrel which shocked the world. Worst hit were the
rising economies, the reliant of west Asians, import of crude oil. These events
were titled the first Energy crisis.
Phases of World Energy Crisis:
Energy is the most volatile in nature in the world market. The various phases of the energy crisis in the world:
First Phase: In 1973, petroleum prices were increased for
the first time by OPEC against OECD. It was a geo-political crisis due to the
Arab & Israel war.
Second Phase: From 1979 to 1980, Islamic revolution in Iran
by Abdullah Khumaini. The supply from Iran drastically reduced. The petroleum
price went from $8 per barrel to $33 per barrel in 1980. The prices finally
settled at $23 per barrel (nationalisation of oil field in Iran).
Third Phase: In 1990, Due to the Gulf war the supply of
petroleum cutoff by Iraq and Kuwait. The petroleum price reached $66 per
barrel.
Fourth Phase: From 1996 to 1997, the petroleum prices fell
to $10 per barrel. The lowest over recorded because of three reasons:
- Food for oil programme in Iraq which increases the supply of petroleum.
- Due to global warming, winters were mild in temperate regions that decreased the demand of energy from developed nations.
- South East Asian financial crisis which reduces demand for petroleum.
Various Dimensions of Energy Crisis:
- Economic: Energy crisis can have negative impacts on economic growth and development, leading to increased costs for businesses and consumers, reduced productivity, and loss of jobs.
- Environmental: Energy crisis can lead to increased emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants, causing environmental degradation and contributing to climate change.
- Social: Energy crisis can lead to increased social inequality, as access to affordable and reliable energy sources is not evenly distributed across the population.
- Geo-political: Energy crisis can lead to political instability, as governments and international organizations struggle to find solutions to the problem.
- Security: Energy crisis can pose risks to national security, as reliance on foreign energy sources can make a country vulnerable to economic and political coercion.
- Technological: Energy crisis can spur the development of new technologies and energy sources, leading to innovation and progress in the energy sector.
Causes of Energy Crisis:
- Increasing global demand for energy.
- Limited availability of fossil fuels.
- Inefficient energy production and consumption.
- Dependence on a few major energy sources.
- Political instability in major energy-producing regions.
- Climate change and environmental concerns.
- Lack of investment in renewable energy sources.
- Inadequate infrastructure for energy distribution.
Impact of Energy Crisis:
- Higher energy prices have contributed to painfully high inflation.
- Some factories to curtail output or even shut down.
- More Unemployment.
- Increase poverty.
- Slowed economic growth heading towards severe recession.
- People all throughout the world are unable to bear the rising costs as the prices for commodities like gasoline, fertiliser, and food rise.
- As a result, the impact of rising energy prices on the humanitarian crisis and food shortages is unprecedented.
Solutions for Energy Crisis:
- Intervention by the security council.
- OPEC and OECD better bargain between them.
- UN Assembly discussion.
- Increasing the efficiency of energy production and consumption through technology and infrastructure improvements.
- Investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power.
- Implementing energy conservation measures such as reducing waste and improving insulation in buildings.
- Investing in energy storage technology to help smooth out the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources.
- Developing and promoting alternative fuels such as biofuels or hydrogen.
- Increasing the use of energy-efficient appliances and vehicles.
- Investing in energy-efficient public transportation systems.
- Promoting energy conservation and sustainability through education and public awareness campaigns.
An energy crisis is any significant disturbance in the
supply of energy resources in an economy. The literature generally refers to
one of the power sources used at a specific time and location, notably those
that provide a country-wide energy infrastructure and those used as the fuel
for product development. The current epidemic and population increase have
caused a spike in the world's energy demand. Because non-renewable energy sources
like coal and natural gas are being used up quickly, society is currently
experiencing an energy crisis. All of the issues can be resolved by the growth
of green energy or greenflation, however it will take some time.
Reference: IEA

Post a Comment
Post a Comment
Thanks...keep in touch 🤟